Elementary Lesions
Elementary Lesions
Honeycombing
Characteristics
-
Clustered cystic airspaces with well defined walls, measuring 2-10 mm in diameter, sometimes reaching 25 mm, usually in subpleural regions
Diagnostic Orientation
-
Intralobular reticulation
-
Traction bronchiectasis and bronchiolectasis
-
Loss of lobar volume
-
Fissured distortion
1. Honeycombing
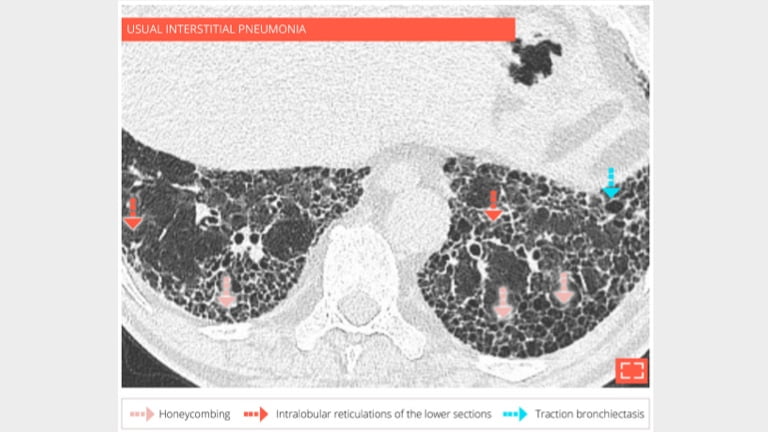
Subpleural honeycombing forming several layers of cysts in a 73-year-old man with usual interstitial pneumonia.
2. Honeycombing
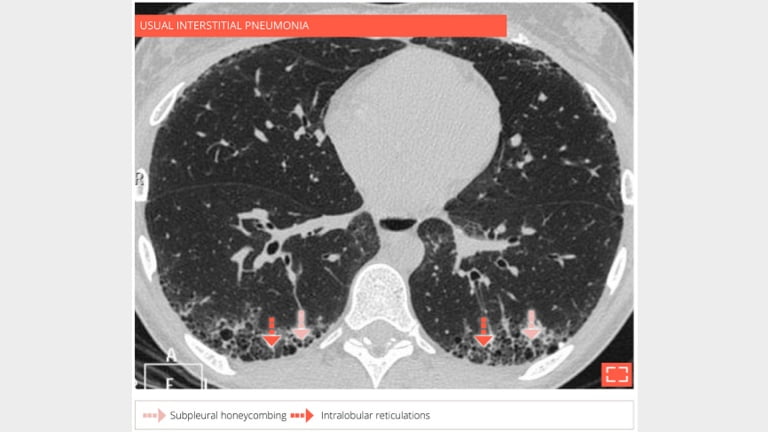
69-year-old man with usual interstitial pneumonia. Subpleural honey combing is associated with reticular pattern.
3. Honeycombing
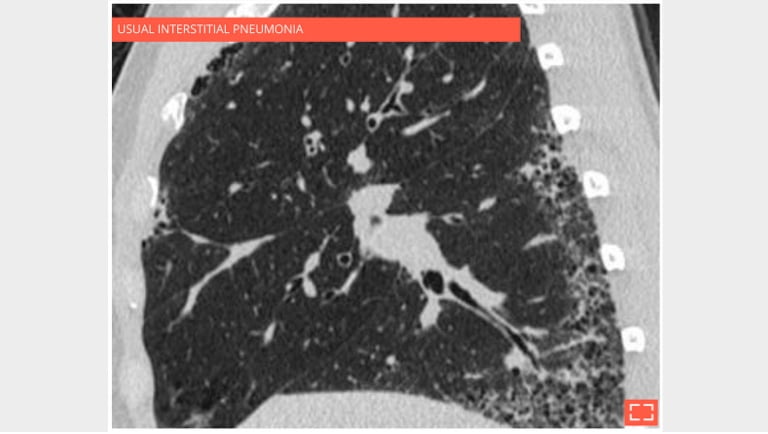
Sagittal reformation in the same patient showing the preferential subpleural and basal distribution.
4. Honeycombing
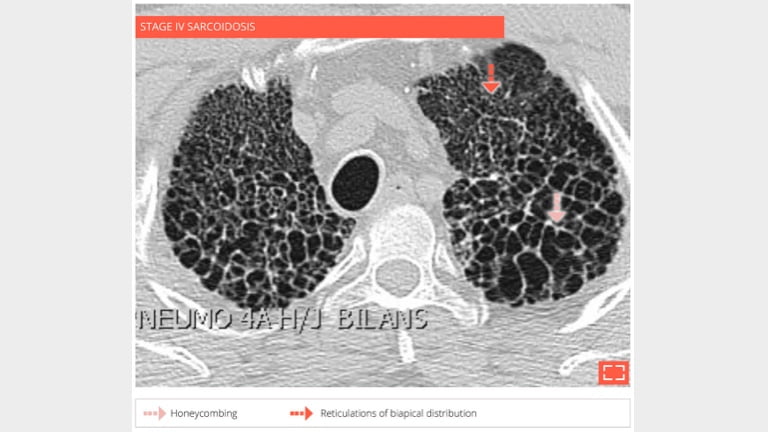
56-year-old man with history of sarcoidosis. Typical honeycombing in a upper lobe distribution.
5. Honeycombing
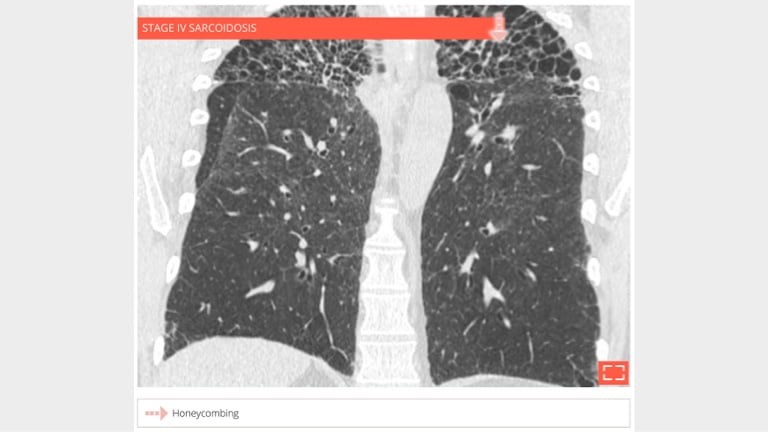
- Coronal reformation in the same patient shows the association of honeycombing and reticulation in lung apices.
- Distribution of fibrosis to apices makes this fibrosis incompatible with UIP.
